This blog provides various aspects that need to be considered while developing scalable and robust enterprise applications. I will discuss the following areas of Enterprise Applications development and considerations.
- Application should have capabilities to accommodate growth and scale, modular to enhance or add new functionalities, support gradual or abrupt surge etc. At the same time, it should be seamless for users and efficient for the organizations.
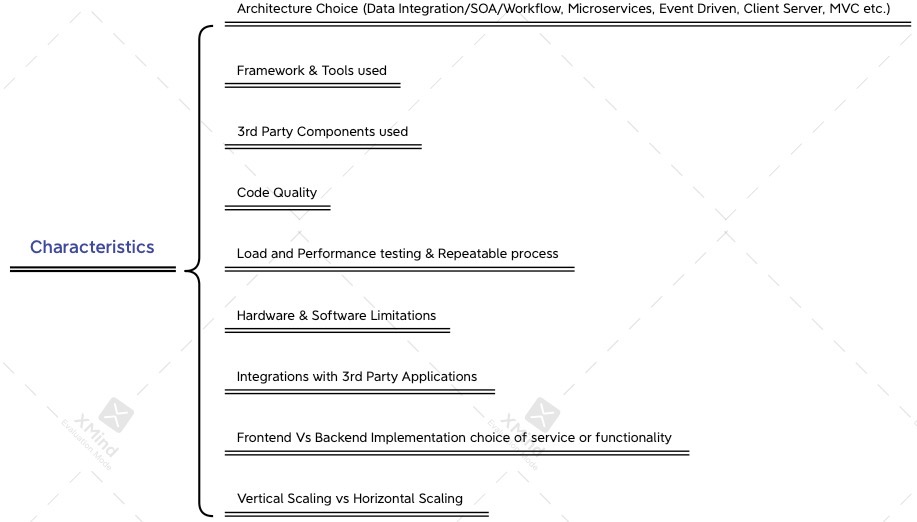
- Factors or Characteristics that influence the application scalability & robustness
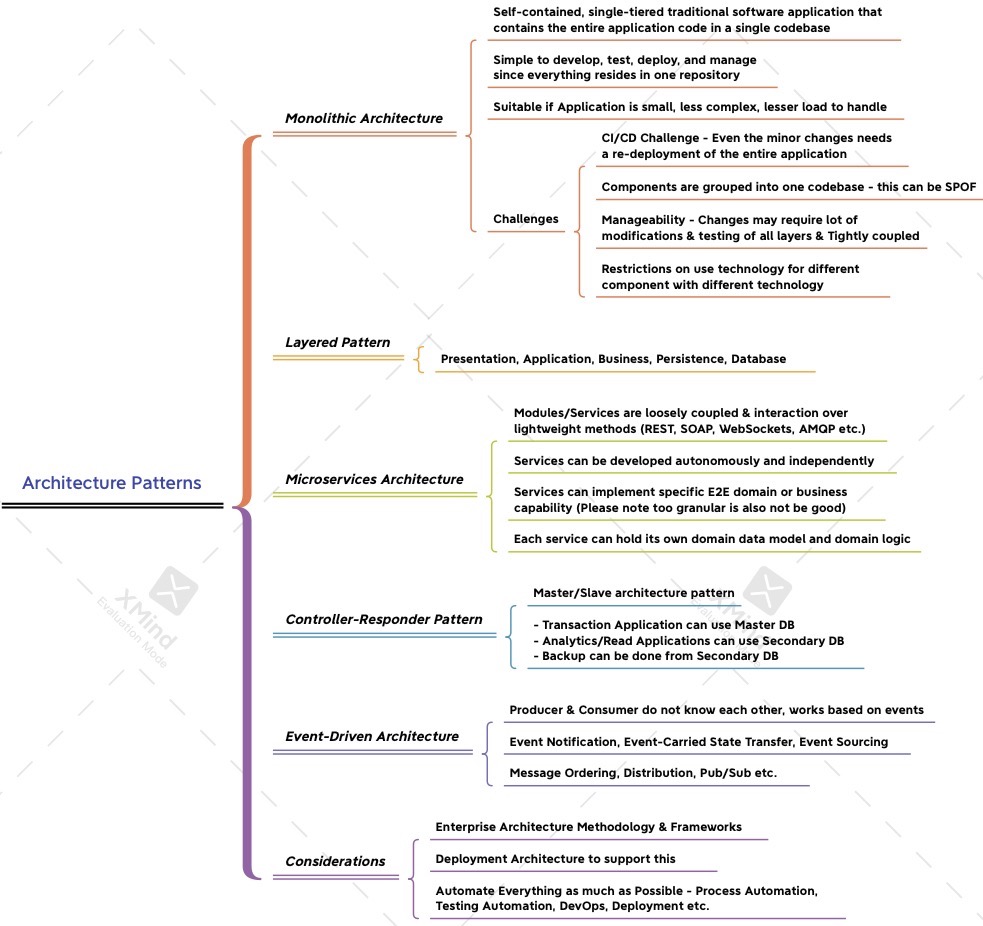
- The different architecture patterns, its pros and cons and considerations. The standard architecture brings many advantages for development, better flexibility of the system for scaling.
- How to build scalable enterprise applications. What are the different Design Methods to consider across various components of the applications?
- Different Technology, tools, framework, software that can be used while designing enterprise applications. Mostly we will high light opensource technologies as much as possible.
- Basic Architectural Design principles to consider for designing large scale applications
In the end, I will provide very high-level architecture considering most of the aspects discussed in this blog. I will provide information in the form of mind maps which I captured for the above areas.
1. What are the Design Principles to be considered?
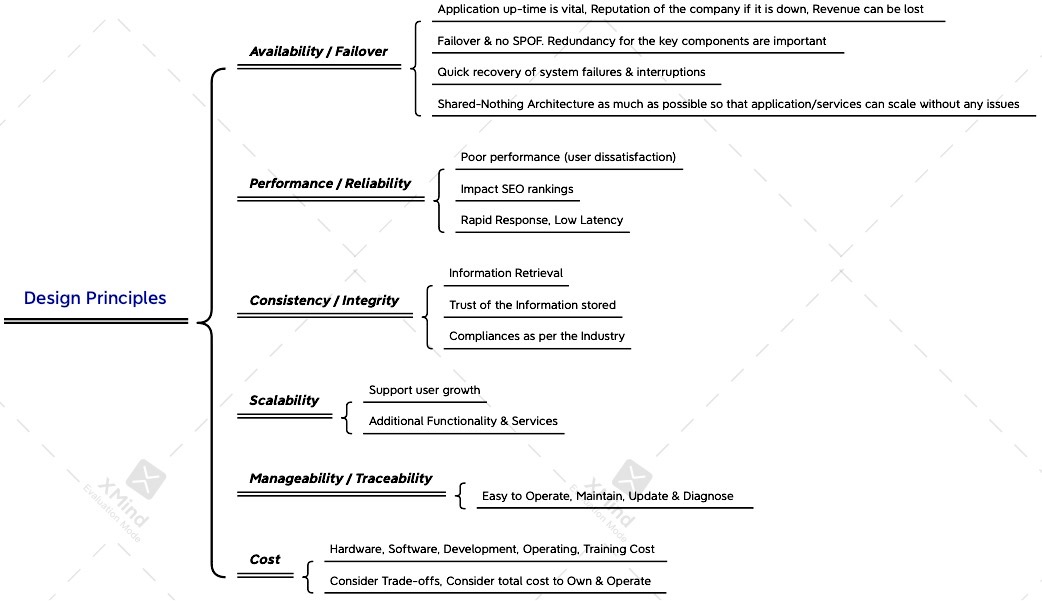
2. What are the factors that influences the application scalability & robustness?
3. Architectural Patterns and Considerations
4. What are the Design Methods to be considered for various components of the application?
- Authentication & Authorization:

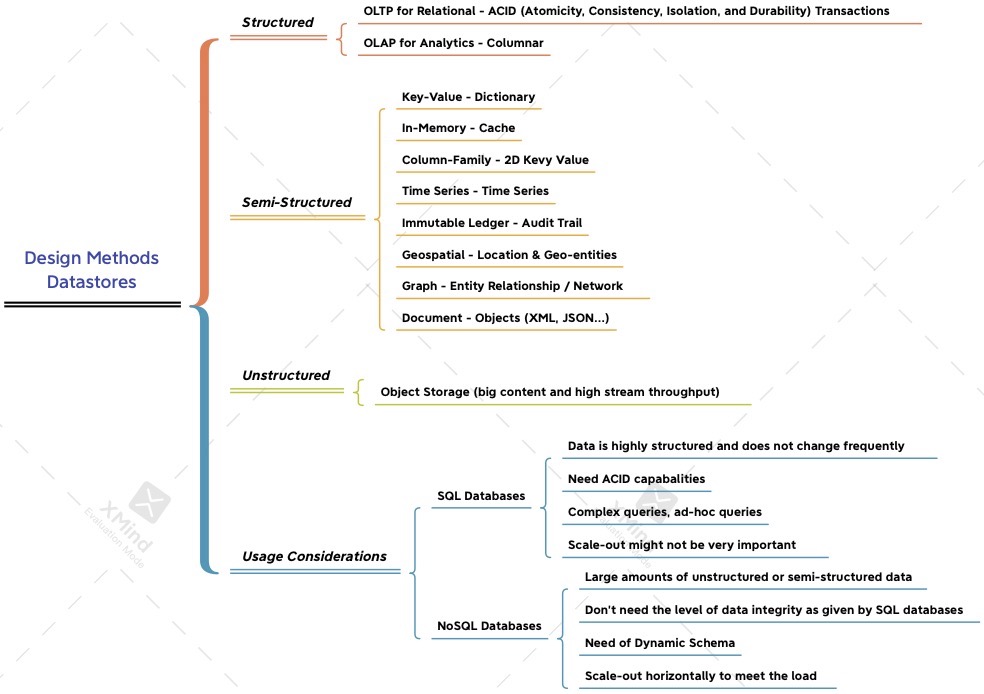
- Datastores:
- Other Design Method Considerations:

5. Technology, Tools, Framework, Software to use
In the below mind map, I tried to give as much as possible open-source implementations. However, in some cases, there are vendor specific implementations as well.
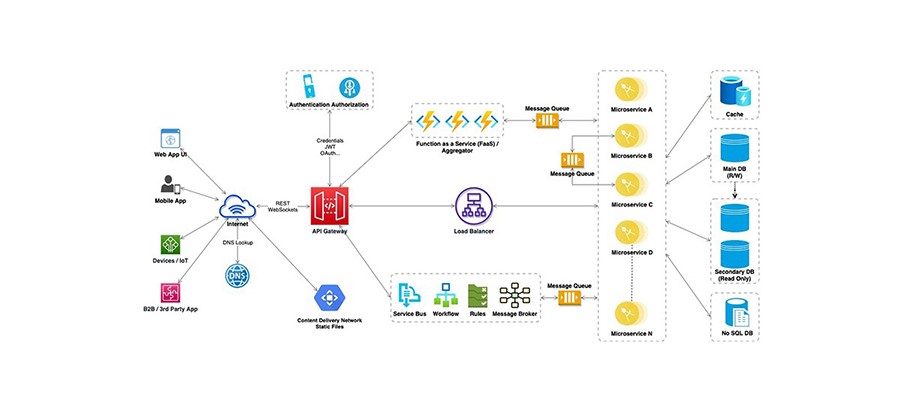
6. Reference Architecture
Below diagram provides the reference architecture for building Enterprise Application especially Web Applications. This covers many of the architecture or design components discussed in this blog. However, there might be some of the design components omitted as well as it is difficult depict everything in the diagram.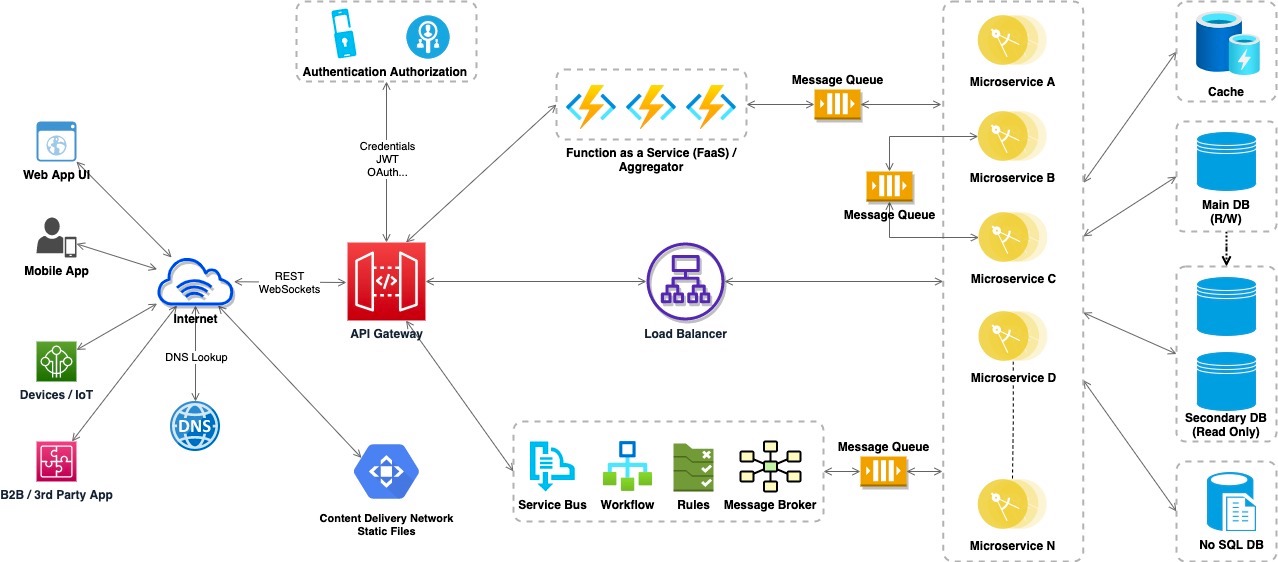
7. Conclusions
- Technology – Choose right technology, tool, framework, software, hardware, database, storage etc.
- Distribute – While scaling the application up, distribute as much work as you can away from the core
- Choose asynchronism methods over synchronous – so that processing threads are not locked, and application resources are optimally used
- API first – think web application as of API service.
- Statelessness in app as much as possible unless there is good reason to have state/store sessions – design components stateless, as they can easily be redistributed to support horizontal scaling
- Make sure to cache – they significantly improve scalability and performance
- Use Queues wherever possible to make the task/messages atomic, retry/retrieve if fails etc.
- Process Automation – Automate the business processes, workflow, rules etc.
- Database Scaling – Through Partitioning, Indexing, Read Replica, Offload database backup etc.
- Design for Maintenance – monitor it and provide regular updates
- Choose a horizontal scale over a vertical – With a horizontal scale, we can just add another server rather than upgrade the existing one
- Load Balancing – Both front end and back end
- Scalability vs Failover – Don’t rule out failures and design to prevent SPOF
- Deployment – CI/CD, ability to rollback deploy, automate as much as possible everything to deploy and run etc.
- Testing Approach – Performance Testing, Load Testing, Failover/DR Testing, Functional Testing Automation. Make this repeatable process and have strategy to test these frequently whenever required.