Before exploring the significance of Virtual DOM we need to get an idea on the concept of DOM and the limitations in traditional DOM manipulation.
What is DOM?
The DOM is a W3C (World Wide Web Consortium) standard
The DOM defines a standard for accessing documents: “The W3C Document Object Model (DOM) is a platform and language-neutral interface that allows programs and scripts to dynamically access and update the content, structure, and style of a document.”
What is HTML DOM?
The HTML DOM is a standard object model and programming interface for HTML.
It defines:
- The HTML elements as objects
- The properties of all HTML elements
- The methods to access all HTML elements
- The events for all HTML elements
In other words:
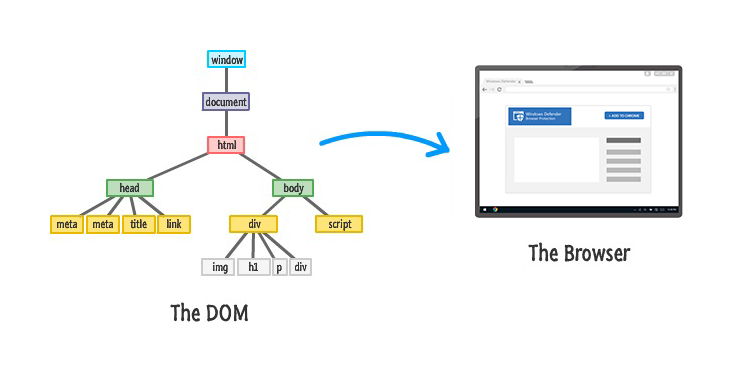
The HTML DOM is a standard for how to get, modify, add or delete HTML elements. At the basic level, a website consists of an HTML and CSS document. The browser creates a representation of the document in a tree structure of objects known as Document Object Model(DOM). The document helps JavaScript to directly access and manipulate the content, structure, and styles of the document.
HTML DOM Model
The DOM represents a document with a logical tree structure. Each branch of the tree ends in a node, and each node contains HTML objects. So it is the owner of all other objects in your webpage and If you want to access any HTML object on your webpage you always have to start with the document. DOM properties and methods allow programmatic access to the tree. Nodes have event handlers attached to them, once an event is triggered using JavaScript, the event handlers enable us to access and modify our website.
Limitations
Taking JavaScript application data and rendering it into a browser is a costly operation. Let’s consider an example, Imagine a complex UI with thousands of DOM nodes. The user inputs a data in a form field and you want to update a <p> tag’s content to reflect this. With Javascript, you have to change all the DOM nodes (remember we have thousands of them) to see the change in just one node. So “DOM manipulation is expensive” in the traditional web world.
To overcome the limitations in traditional DOM the concept of the Virtual DOM came into existence.
What is Virtual DOM?
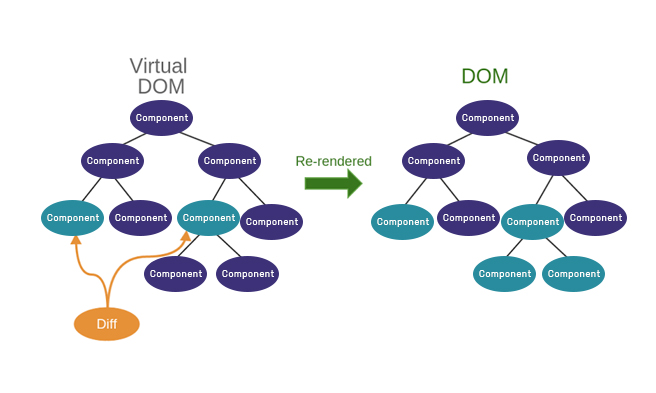
The virtual DOM is a programming concept where a virtual representation of a User Interface is kept in memory and synced with the Real DOM. In React context, the Virtual DOM is React’s local and simplified copy of the HTML DOM. ReactJS is the first framework to take this to an obvious conclusion: optimizing for DOM manipulation leads to a fast library, and in this case, a library which enables web applications that require very little code. ReactJS works by storing the state of your application internally, and only re-rendering your content into the browser (the DOM manipulation) when the state changes. You interact with ReactJS by telling it when the state has changed and ReactJS handles all the visual changes to your application for you. Consider the above example, React sees the change you want to make and only re-renders the <p> tag. This one behavior leads to massive performance increases and is the reason for React to become more popular.




